A Beginner's Guide to Mastering Abstract Data Types in JavaScript

A Beginner's Guide to Mastering Abstract Data Types in JavaScript
Grasping the concept of Abstract Data Types (ADTs) is key to enhancing your programming problem-solving abilities. ADTs offer a structured approach to organizing and managing data, simplifying the process of creating efficient solutions. In this blog post, we’ll cover the fundamentals of ADTs and demonstrate how to implement popular types like stacks, queues, and linked lists in JavaScript. Let’s get started!
What Are Abstract Data Types (ADTs)?
Abstract Data Types (ADTs) are conceptual models used to organize and manipulate data. Unlike concrete data structures, ADTs emphasize what operations can be performed rather than how those operations are implemented. For instance, a stack enables adding and removing data in a "last-in, first-out" (LIFO) manner, but the underlying implementation can differ.
Key Characteristics of ADTs
1. Abstract Nature: ADTs focus on the behavior rather than the implementation.
2. Encapsulation: They hide implementation details and expose only the required operations.
3. Flexibility: ADTs can be implemented in different ways using various data structures.
Why Are ADTs Important in JavaScript?
JavaScript is a versatile programming language used for web development, backend development, and more. While JavaScript’s standard library doesn’t include many advanced data structures, understanding and implementing ADTs can:
- Improve your algorithmic thinking.
- Enhance the performance of your applications.
- Provide reusable and maintainable code structures.
Common Abstract Data Types and Their Implementations in JavaScript
Stack
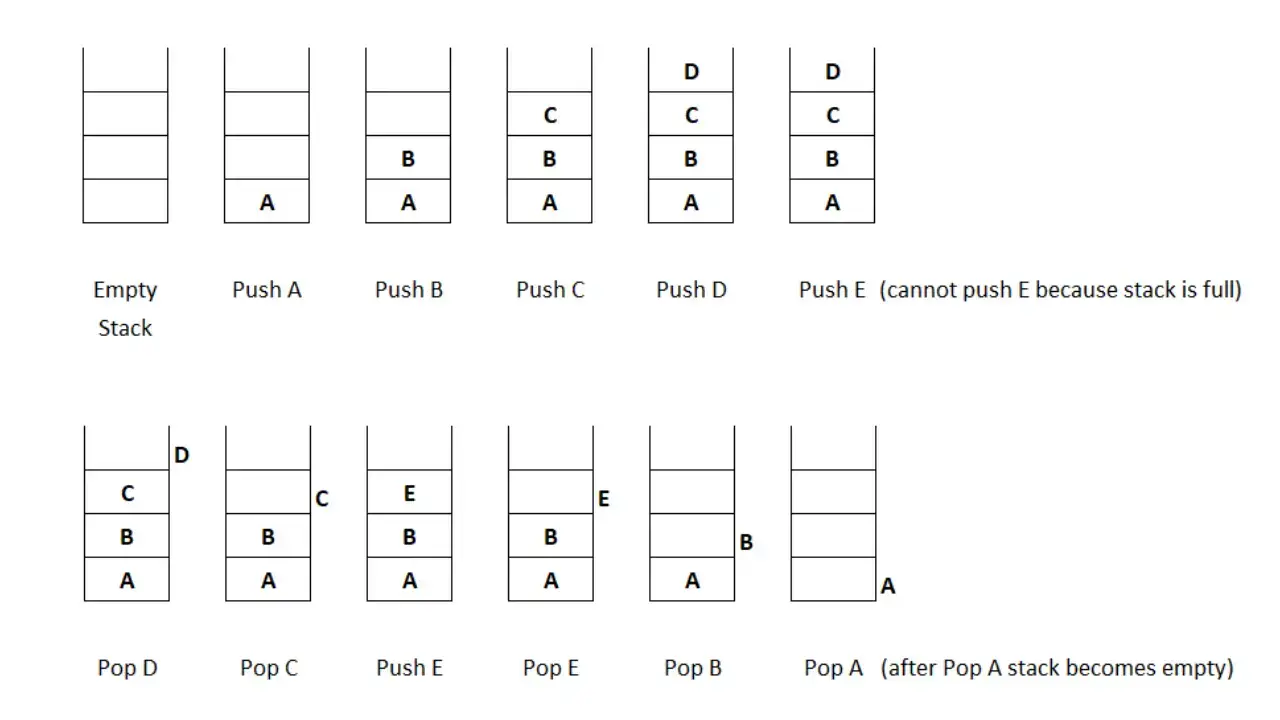
A stack is an ADT that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. Imagine a stack of plates: the last plate added is the first one to be removed.
Operations:
- Push: Add an element to the stack.
- Pop: Remove the top element from the stack.
- Peek: View the top element without removing it.
- IsEmpty: Check if the stack is empty.
JavaScript Implementation:
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack is empty");
}
return this.items.pop();
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack is empty");
}
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
}
// Example usage
const stack = new Stack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
console.log(stack.peek()); // Output: 20
stack.pop();
console.log(stack.peek()); // Output: 10Queue
A queue is an ADT that follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. Think of a line at a store: the first person in line is the first to be served.
Operations:
- Enqueue: Add an element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove the front element from the queue.
- Peek: View the front element without removing it.
- IsEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Queue is empty");
}
return this.items.shift();
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Queue is empty");
}
return this.items[0];
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
}
// Example usage
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(20);
console.log(queue.peek()); // Output: 10
queue.dequeue();
console.log(queue.peek()); // Output: 20
Linked List
A linked list is an ADT where each element (node) contains data and a reference (link) to the next node. This structure allows dynamic memory allocation and efficient insertions/deletions.
Types:
- Singly Linked List: Each node points to the next node.
- Doubly Linked List: Each node points to both the next and previous nodes.
Singly Linked List Implementation:
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
add(element) {
const newNode = new Node(element);
if (!this.head) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
remove(element) {
if (!this.head) {
throw new Error("List is empty");
}
if (this.head.data === element) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.size--;
return;
}
let current = this.head;
let prev = null;
while (current && current.data !== element) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (!current) {
throw new Error("Element not found");
}
prev.next = current.next;
this.size--;
}
print() {
let current = this.head;
let result = [];
while (current) {
result.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
console.log(result.join(" -> "));
}
}
// Example usage
const list = new LinkedList();
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.print(); // Output: 10 -> 20 -> 30
list.remove(20);
list.print(); // Output: 10 -> 30
Conclusion
Mastering Abstract Data Types (ADTs) in JavaScript enables you to design more efficient and maintainable code. Stacks, queues, and linked lists are just a few examples of ADTs that form the foundation of more advanced data structures. By practicing these implementations, you’ll strengthen your understanding of algorithms and be better equipped to tackle real-world programming challenges.
FAQ's
What are the abstract data types in JavaScript?
An Abstract Data Type (ADT), as the name suggests, is an abstract understanding of a data structure. An ADT is defined through its behavior and characteristics, particularly in terms of what data can be stored into it, the operations that can be performed on this data, and the behavior of these operations.
Is it good to learn DSA in JavaScript?
Yes. DSA is a core aspect of software engineering, and anyone learning software should have knowledge in DSA whether they are software engineer or mastering in web development, blockchain engineering, etc. It will cause you to be a better problem solver, a better coder, and a better developer in general.
How many types of JS are there?
JavaScript has seven built-in types: null , undefined , boolean , number , string , object , and symbol . They can be identified by the typeof operator. Variables don't have types, but the values in them do. These types define the intrinsic behavior of the values.
Which is better for DSA, JavaScript or C++?
C++: If your primary goal is mainly focusing in problem solving using DSA and clearing DSA rounds as part of your campus placements, C++ is the right choice as C++ is known for its speed and efficiency, making it an excellent choice for DSA.
What is minus zero in JavaScript?
Floating point numbers include a sign bit (0 for positive, 1 for negative). In the case of +0 , the sign bit is 0 while in the case of -0 the sign bit is 1.



















0 Comments
No Comment Available